Explanation of How to Read Motor Performance Curves and T-N Curves
Many engineers who have just started working with motors may have a hard time with performance curves. In order to get the most out of a motor's performance, it is important to read the performance curve accurately. It may seem difficult at first glance, but once you have the basics down, you will have an accurate understanding of the properties of the motor, which can be very useful when selecting a motor.
This article therefore provides a basic view of the performance curve, as well as the T-N curve (torque curve), which is often included with the performance curve of a motor.
contents[非表示]
- 1.How to Read a Motor Performance Curve
- 1.1.Rotation-torque Line (Solid blue line in the performance curve example)
- 1.2.Current Line (Solid orange line in the performance curve example)
- 1.3.Output Line (Dashed black line in the performance curve example)
- 1.4.Efficiency Line (Solid black line in the performance curve example)
- 2.How to Read the T-N Curve (Torque Curve) of a Motor
- 3.Changes in the T-N Curve for Different Motor Drive Voltages
- 4.How to Select a Motor using Performance Curves and T-N Curves
- 5.Points Often Overlooked in Motor Selection
- 6.Summary
How to Read a Motor Performance Curve
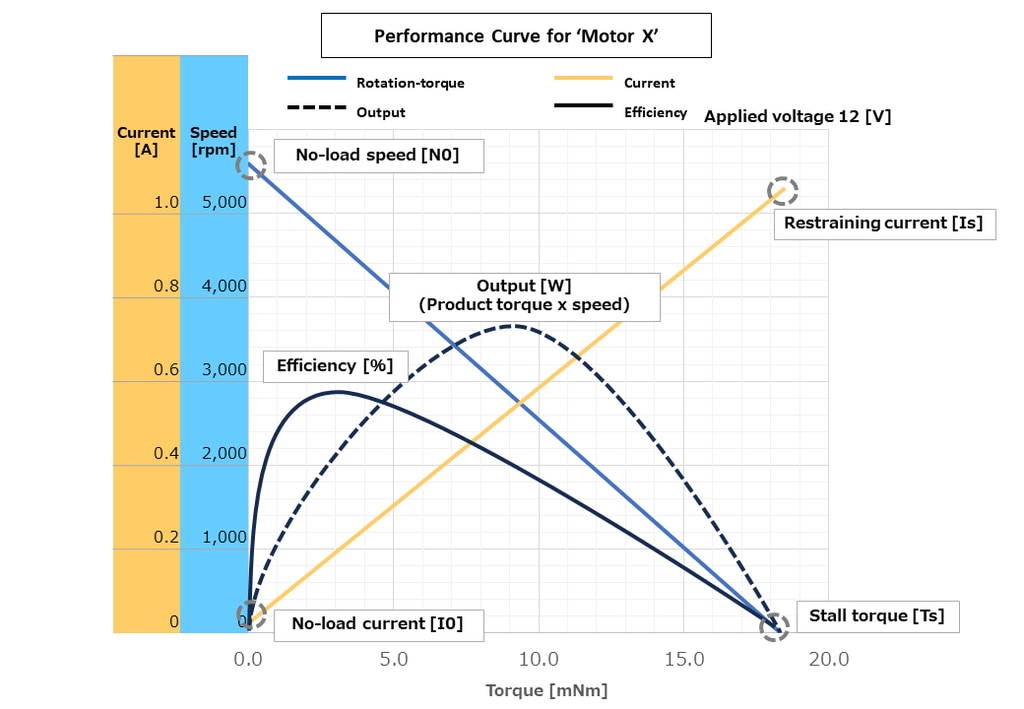
Example of a performance curve
Motor performance curves are often expressed using the torque reference method, which allows the speed, current, output and efficiency to be determined based on torque. Torque refers to the motor's rotational force and is expressed in Nm (Newton meters), or sometimes in mNm (milli-Newton meters), as in the performance curve example above. The horizontal axis shows the torque, the vertical axis shows the number of rotations (speed) and the current value, indicating the correlation between these values.
The following is an explanation of each line in the performance curve.
Rotation-torque Line (Solid blue line in the performance curve example)
This line represents the relationship between speed and torque and is sometimes referred to as the T-N curve. The relationship between speed and torque is inversely proportional, so it is depicted as a straight line with a downward right shoulder. From this line, the maximum speed and torque that the motor can produce can be read.
No-load speed [N0], as the name implies, represents the maximum speed in the absence of load, i.e. with zero torque. Stall torque [Ts] is the torque at stall, i.e. the maximum torque that the motor can produce when the rotation stops after increasing the motor load.
Current Line (Solid orange line in the performance curve example)
This line represents the current flowing in the motor from the no-load state to the restrained state and is sometimes referred to as the T-I curve. No-load current [I0] is the current value with no load.
Theoretically, the current would be zero without a load, but in reality, the performance diagram shows a slightly larger value than zero due to weak current flow caused by iron loss and friction. The restraining current [Is] refers to the current value when the motor is restrained, i.e. when the motor has stopped rotating.
Output Line (Dashed black line in the performance curve example)
Output [W] is expressed as the product of torque and speed. Normally, the output is maximized at half of the no-load speed. The point at which the output is maximized is called ‘instantaneous maximum output’, but it should be noted that this is different from ‘rated output’, which is the maximum value of output that the motor can continuously and stably deliver.
The torque value at rated output is called ‘rated torque’ and the speed is called ‘rated speed’. These values are usually listed in the performance table of the motor and should be checked in conjunction with the performance curve.
Efficiency Line (Solid black line in the performance curve example)
The output divided by the voltage is the efficiency [%]. The point at which the motor is most efficient in relation to its power consumption is called the ‘maximum efficiency’.
Note that the performance curve example shown here is for an applied voltage of 12 V, as indicated in the top right corner of the diagram. As the performance curve also changes when the voltage changes, it should be checked that there is no discrepancy between the voltage you want to use and the performance curve you are looking at.
How to Read the T-N Curve (Torque Curve) of a Motor
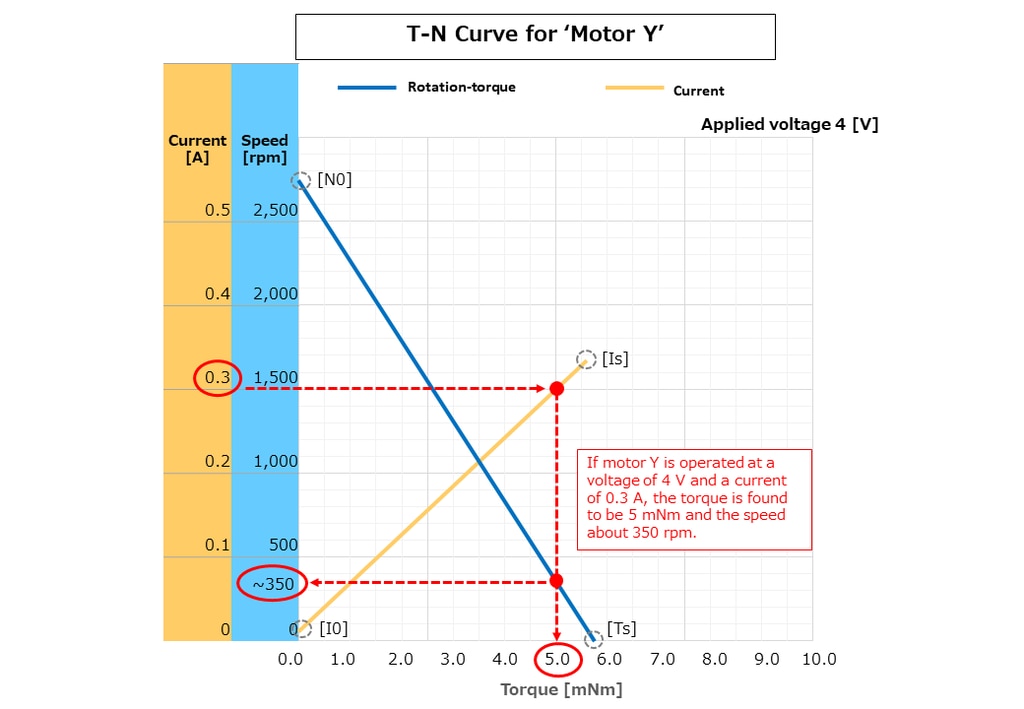
Example of a T-N curve
The T-N curve is often used in conjunction with the performance curve to show the performance of a motor. This curve shows the relationship between the torque that the motor can exert in relation to the current flow and the number of rotations (speed) per current flow, which is also called a torque curve.
For example, if motor Y is operated at a voltage of 4 V and a current of 0.3 A, as in the T-N curve example above, the torque and speed can be determined by using the following procedure.
Reading torque and speed in the above curve:
- Find the 0.3 A point on the current line.
- The torque value on the horizontal axis at the above point indicates that a load of 5 mNm is being applied.
- On the vertical rotation-torque line, the number of rotations (speed) at the above torque value of 5 mNm indicates that the motor rotates at approximately 350 rpm.
Changes in the T-N Curve for Different Motor Drive Voltages
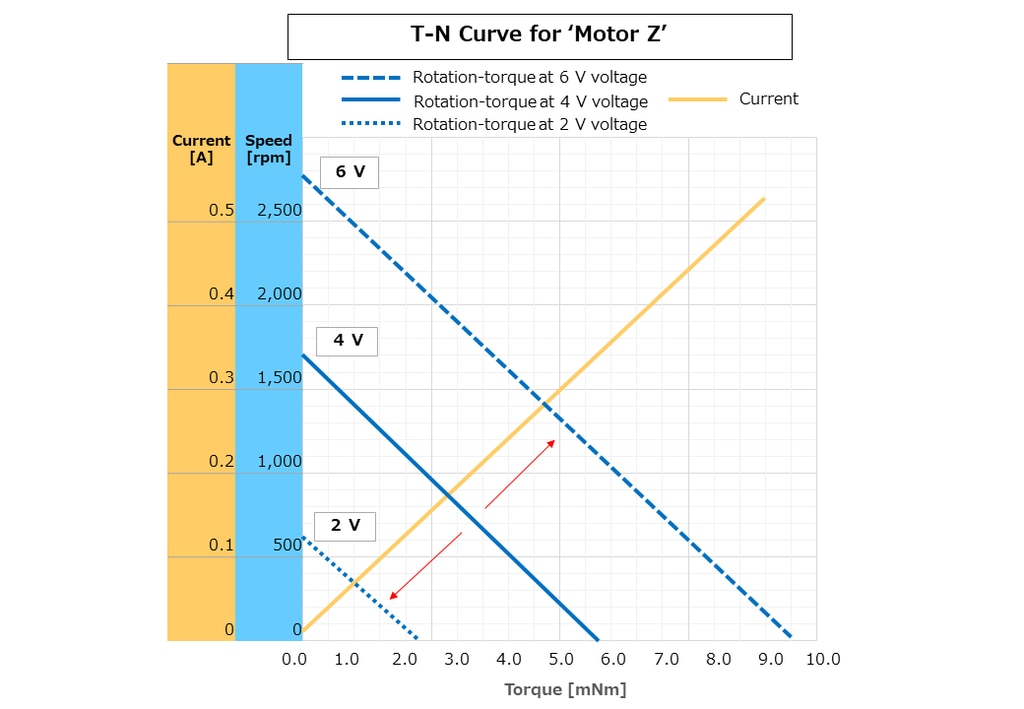
Example of a T-N curve (voltage change)
When the drive voltage of a motor changes, the T-N curve also changes. The motor output (torque x speed) increases in proportion to the voltage, so when the voltage increases, the rotation₋torque line moves directly upwards in parallel. For example, using 4 V as a reference in the above diagram, the rotation₋torque line moves up when the voltage is 6 V and down when the voltage is 2 V.
If you understand how to look at the T-N curve, you will be able to understand how much voltage and current you need to run the motor to meet the required power output.
How to Select a Motor using Performance Curves and T-N Curves
As explained in the ‘How to read the Performance Curve and T-N Curve’, the torque and speed of a motor depend on the voltage and current of the power supply. If you know the value of the power supply you handle, i.e. the voltage and power, the estimated torque and estimated speed when the motor is driven by that power supply will also become clear.
When selecting a motor, confirm the value of the power supply to be used, check the performance of the motor published by the manufacturer and choose a motor that can meet the required specifications.
Points Often Overlooked in Motor Selection
When selecting a motor, there is a tendency to choose a motor based on the maximum number of stable outputs it can provide, such as rated torque or rated speed, but it is also very important to consider whether the motor has sufficient torque at motor start-up, i.e. the maximum torque, the constraint torque [Ts].
If the starting torque [Ts] is insufficient, the equipment will start up slower, which may reduce work efficiency when used in industrial applications. Therefore, as well as the rated torque and rated speed, the restraining torque is another item that should be checked carefully in the motor's performance table.
In addition, motor performance curves and T-N performance tables generally show torque on the horizontal axis and current value and speed on the vertical axis, but in some cases the vertical and horizontal axes are reversed, so care should be taken not to misread them.
Summary
This article provided the following information on how to read motor performance curves and T-N curves:
- How to Read a Motor Performance Curve
- How to Read a T-N Curve (Torque Curve)
- How the T-N Curve Changes when the Drive Voltage of a Motor is changed
- How to Select a Motor using Performance Curves and T-N Curves
- Points Often Overlooked in Motor Selection
Each manufacturer that sells motors publishes performance curves and T-N curves for motors, so learning the correct way of reading them will be useful when choosing a motor.
In addition, a more accurate selection can be made by being aware of the power supply that will be used and checking the performance curve to identify the estimated torque and estimated speed. Furthermore, when selecting a motor, consideration should also be given to the restraining torque, which can help prevent equipment start-up failures before they cause a performance loss.
Mabuchi Motor manufactures and sells a wide variety of small motors. Performance tables and features are available for each product on our website and in our catalog, so engineers and developers who are considering purchasing a motor are encouraged to check these items beforehand.