How to Utilize Hollow Frameless Motors
Hollow frameless motors are attractive because they can save space in the application and enable a highly flexible design. However, due to their different shape compared to commonly used motors, choosing peripheral equipment and fixing methods can be a challenge, making implementation difficult for some.
This article aims to address any concerns you may have about using hollow frameless motors and installing them smoothly.
contents[非表示]
What is Hollow Frameless Motor?
Among hollow motors that have a hole in the center, the type that includes only a stator and rotor is known as a hollow frameless motor. These motors are commonly used in the joints of collaborative robots and devices with integrated structures.
Efficient cable and component arrangement is crucial when multiple motors and peripheral equipment are employed in a device. Hollow frameless motors are beneficial in this regard as they can effectively utilize limited space by allowing wiring through their central holes.
Related article: What is a Hollow Motor? Explanation of the Main Advantages and Applications
Concerns in Utilizing Hollow Frameless Motors
The following two points are common challenges in utilization of hollow frameless motors.
Point 1: Lack of knowledge on selecting peripheral equipment like drivers, sensors, and gear reducers
Point 2: Lack of knowledge on how to fix the stator
This section will explain how to solve these concerns.
Point 1: Lack of knowledge on selecting peripheral equipment like drivers, sensors, and gear reducers
Hollow frameless motors are a type of brushless motor and therefore require a driver, which is a type of drive circuit.
In addition, as the motor has a hole in the center, sensors and gear reducers must also be chosen to suit the structure. This section explains the key points in the selection of each peripheral device.
Selecting Drivers
‘EtherCAT Communication Drivers’ are the most common choice for hollow frameless motor drivers. EtherCAT Communication Drivers have extremely high communication speed and responsiveness and enable high-speed and high-precision synchronization control.
Especially in cooperative robots, which are typical applications for hollow frameless motors, precise control such as fine positioning and rotational speed control are often required, so it is recommended to use drivers that support EtherCAT communication.
Selecting Sensors
When installing a sensor for detecting the angle of rotation on a motor, it is necessary to select a hollow-type sensor. Compared to sensors for generally used motors, there are fewer products available, so the choice is limited. It is recommended to select the most suitable for the equipment and operating environment of the end application.
The table below introduces the features of three typical sensor types - optical, magnetic and capacitive encoders - as well as resolvers, which are also used for rotational angle detection.
▼ Features of sensors used to control hollow frameless motors
Type |
Optical Encoders |
Magnetic Encoders |
Capacitive Encoders |
Resolver |
Resolution |
A+ |
A |
A |
B+ |
Environmental Resistance* |
C |
C |
A |
A+ |
Price |
C |
B |
C |
A |
Ease of Installation |
C |
A |
A |
B |
*Resistance to vibration, shock, moisture, oil, dirt and other harsh environmental conditions
Selecting Gear Reducers
To utilize hollow frameless motors, a gear reducer with a hollow structure is also essential. There are various types of gear reducers available, and the most suitable one must be selected according to the purpose.
For example, if the motor is to be used in a mechanism for lifting heavy objects, it is recommended to use a thicker reduction gearbox that can withstand high torques, while a reduction gearbox with a slim design is recommended if weight reduction of the machine body is a priority over torque tolerance.
Point 2: Lack of knowledge on how to fix the stator
While hollow frameless motors, as the name implies, have no frame and can therefore be implemented with a higher degree of freedom than generally used motors, the method of fixing the stator to the housing (chassis) can be challenging.
Three typical fixing methods are presented here.
1.Fixing the stator to the housing and endbell with a fastening force (bolting)
2.Fixing the stator to the housing with adhesive
3.Fixing the stator to the housing by shrink fitting
1.Fixing the Stator to the Housing and Endbell by a Fastening Force (Bolting)
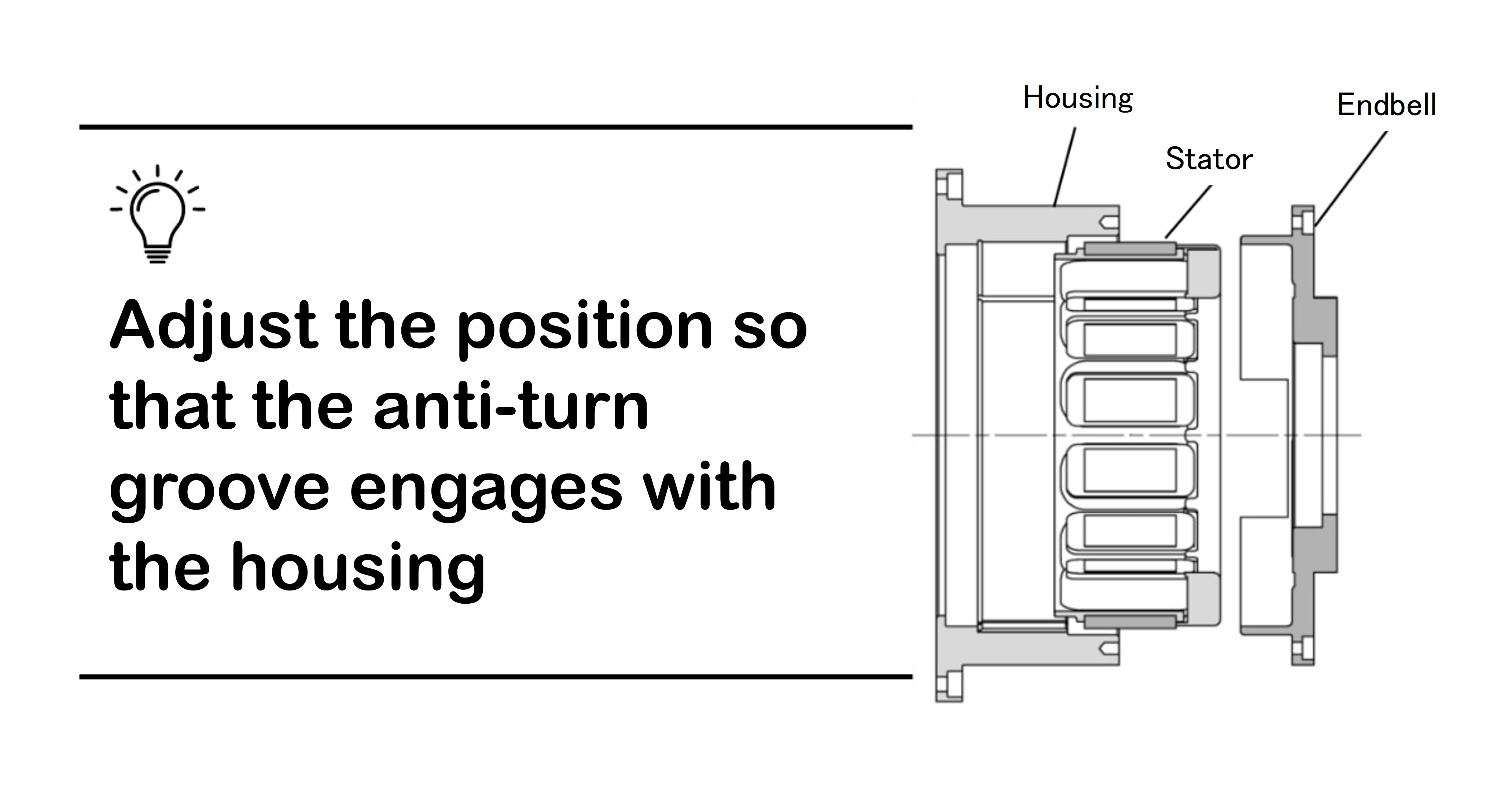
After attaching the stator to the housing, the end bell is attached to the housing and bolted to secure it in place. The advantage of bolted fixing is that it can be easily disassembled if necessary, although it does not have the same fixing force as shrink fitting.
Bolt-tight fixing is recommended for prototypes and for machines that need to be dismantled and inspected regularly.
2. Fixing the Stator to the Housing with Adhesive
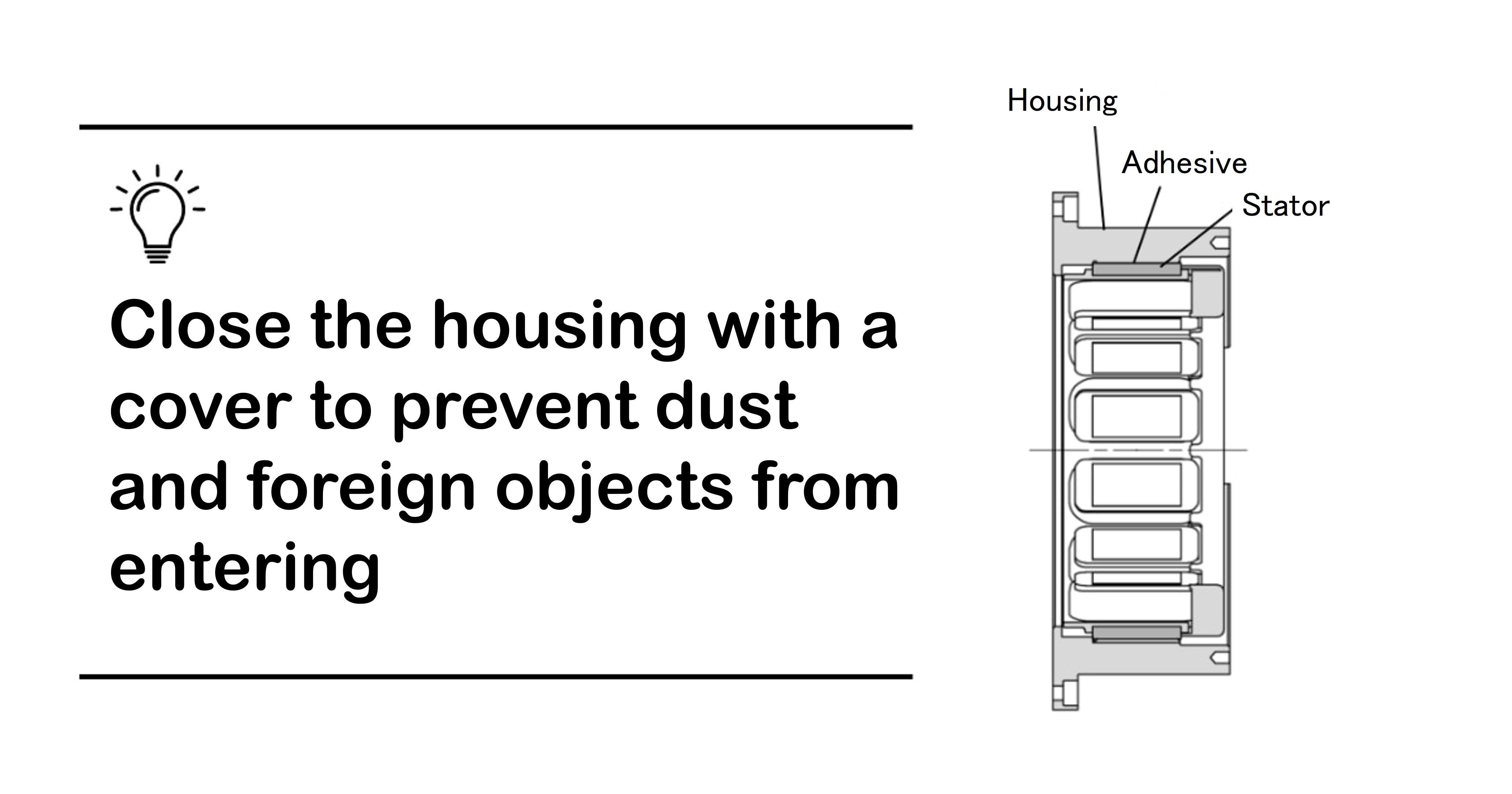
After applying the adhesive evenly to the outer surface of the stator, install the stator in the housing and wipe off any excess adhesive. The key is to select the appropriate adhesive and fitting tolerances to meet the required strength for fixing.
Although not as strong as a shrinkage fit, this is a relatively simple fixing method and requires fewer man-hours. Adhesive fixing is recommended for applications where the fixed part is not subjected to a significant load.
3. Fixing the Stator to the Housing by Shrink Fitting
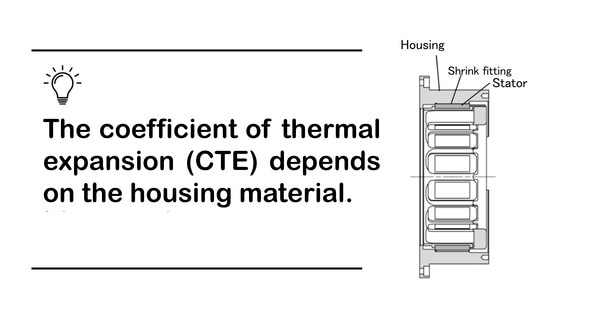
Before the shrinkage fit, check that the housing is thick enough for the torque and has the appropriate surface roughness for shrink fitting. After the housing has been heated to the designated temperature for shrink fitting using a high-frequency coil or similar, the stator can be installed.
Although more time-consuming than adhesives, the advantage of shrinkage fitting is that it provides a very strong fixing force. If the housing is heat resistant and high fixing strength is required, shrinkage fitting is recommended.
For more detailed information, see the instruction manual for hollow frameless motors.
Mabuchi Motor's Hollow Frameless Motors
Mabuchi Motor offers the ‘IA-IB Series’ hollow frameless motors. In addition to being compact, lightweight and energy-saving, the motors feature a low cogging design for smooth rotation.
The line-up includes four different sizes with different rated outputs, which can be selected according to the structure and size of the product.
Summary
This article has explained the following about hollow frameless motors:
- How to Utilize Hollow Frameless Motors
- What is a Hollow Frameless Motor?
- Challenges in Utilizing Hollow Frameless Motors
- Mabuchi Motor's Hollow Frameless Motors
Hollow frameless motors are appealing because they can save space in the application and allow for a highly flexible design, but it is important to understand how to utilize them correctly because their shape differs from that of a generally used motor.
The utilization of hollow frameless motors requires the provision of peripheral equipment such as appropriate drivers, sensors and gear reducers.
Also, as there is no frame, choose an appropriate fixing method for the housing, such as fixing by endbell fastening force (bolting), adhesive or shrinkage fit.
Mabuchi Motor offers the ‘IA-IB Series’ of hollow frameless motors. Our representatives will support you in your purchase, even if you are a first-time buyer.
If you are interested in our products, please feel free to contact us.