What is a Brushless DC Motor? Different types of brushless DC motors and differences with brush DC motors
There are various types of motors, and the most suitable motor depends on the application.
One type of motor is a DC motor, also called a brush DC motor. The electrodes that conduct and commute the current inside the motor are called brushes. While brush DC motors have a lower cost than brushless DC motors, the wear of the brushes over can be a limit in regards of their lifetime.
Brushless DC motors, also colled BLDC motors, offer higher lifetimes and are the only alternative for very high speeds Brushless DC motors are used in a variety of fields, including electrical appliances, drive robots, personal mobility, and medical equipment.
This article provides an overview of brushless DC motors, their differences from brush DC motors, and their types.
contents[非表示]
- 1.How does a Motors Work
- 2.How does a DC Motors Work
- 3.What is a Brushless DC Motors?
- 4.Differences with Brush DC Motors
- 4.1.①Heat Dissipation
- 4.2.②Lifetime
- 4.3.③High Power
- 4.4.④Energy Saving Performance
- 5.Types of Brushless DC Motors
- 6.Types of Sensors for Brushless DC Motors
- 6.1.Encoders
- 6.2.Hall sensors
- 6.3.Resolvers
- 7.Summary
How does a Motors Work
Motor is a device that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy.
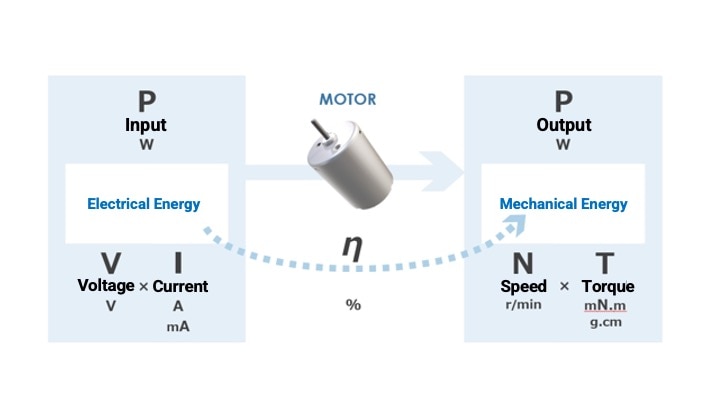
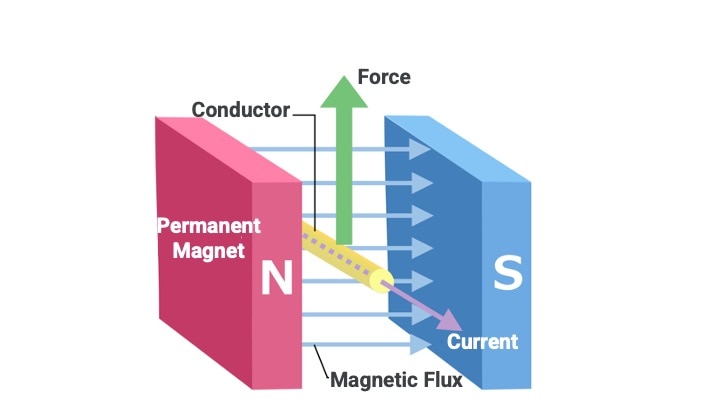
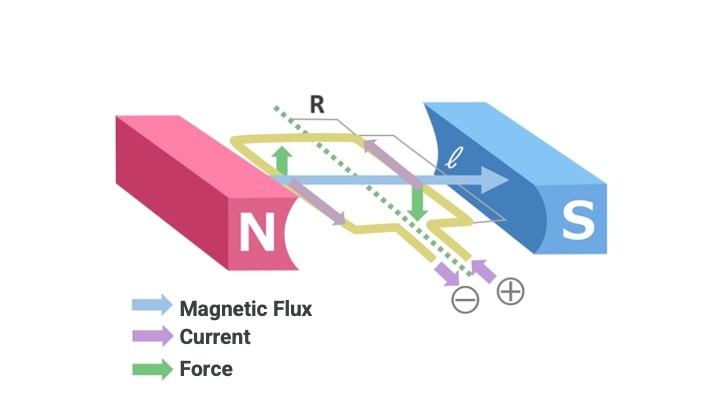
In a motor, a magnetic field is generated by a collection of magnetic fluxes flowing from the N to S poles of facing permanent magnets, and electromagnetic force is generated by passing a current through a coil (conductor) between them.
▼Principle of Electromagnetic Force Generation
How does a DC Motors Work
A DC motor (hereafter referred to as brush DC motor) operates by applying DC power to the coil, which is the rotor.
▼Rotating Mechanism
The commutator (*) attached to the end of the coil and the brushes contact with each other to control the current and rotation.
*A commutator is a component that changes the direction of the current flowing in the coil. In brush DC motors, this component is called a brush and is in physical contact with the coil. The brushes are generally made of carbon due to its good conductivity and low friction coefficient.
What is a Brushless DC Motors?
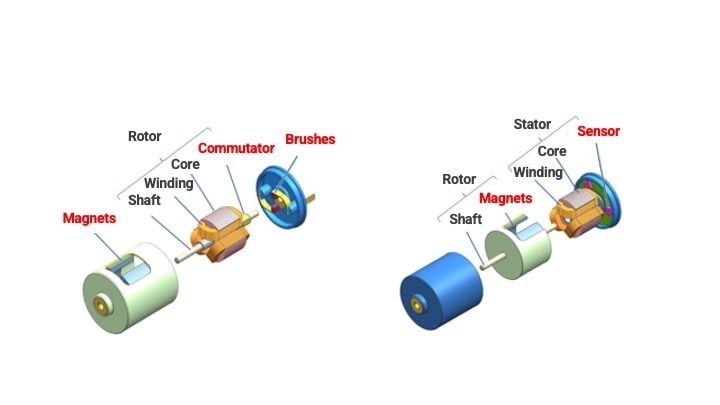
Brushless DC motors do not have a commutator and brushes like in brush DC motors. Instead, the commutation of the phase current is done electronically. To to so, the control electronics must be able to detect the rotor position and synchronize the phase current switch according to the rotor angle. This is usually done with Hall sensors integrated in the motor. More sophisticated control electronics work also without sensors, so sensorless.
Brush DC motors have the advantage of being easy to integrate and control. but Their disadvantage is that due the the wear of the commutation brushes that are in physical contact with the rotor, their lifetime is limited.
Since there are no wear parts on brushless DC motors, their lifetime is superior to brush DC motors.
For more information on the advantages and applications of brushless DC motors, please refer to this article.
Examples of brushless DC motors advantages and Applications
Differences with Brush DC Motors
Brushless DC motors and brush DC motors differ in other ways besides the presence or absence of commutator and brushes. Here are four differences between the two.
Item |
Brush DC Motor |
Brush DC Motor |
Heat Dissipation |
Low |
High |
Lifetime |
Relatively short |
Longer than brush DC motors, in particular at high speeds |
High Power |
Difficult to achieve |
Easy to achieve |
Energy Saving Performance |
Good |
Superior to brushed DC moto as is are less friction thanks to the suppression of the commutation brushes |
①Heat Dissipation
Brushless DC motors have higher Heat Dissipation than brush DC motors, so their performance is less susceptible to degradation and relatively stable even after continuous operation.
Heat is generated when current passes through a motor. Brush DC motors have a layer of air between the coils and the motor case, which prevents the heat generated from dissipating outside. As the temperature inside the motor rises, it becomes difficult for current to flow through the coils, resulting in a gradual decrease in rotation speed.
On the other hand, in brushless DC motors, the coils and motor case are tightly sealed together, which prevents the formation of an air layer, allowing the heat generated by the coils to be efficiently dissipated.
②Lifetime
As mentioned previously, the lifetime of a brush DC motor is shorter than the one of brushless DC motors as the latter does not have brushes that wear out over time.
Therefore, brush DC motors are worn by the brushes and require periodic maintenance or motor replacement. Brushless DC motors, however, can continue to be used for a relatively long time due to the lack of friction.
In addition, in applications where Mabuchi Motor's brush DC motors are installed, Long lifetime is achieved without the need for maintenance or replacement. Like brushless DC motors, they can be used for a long period of time.
The only limiting factor of a brushless DC motor in regards of its lifetime will be the lifetime of the bearing that is dependant on its load conditions in use and its operating temperature. The higher the temperature, the lower the lifetime. High-end brushless DC motors, as proposed for example by Mabuchi Motor Electromag, use high quality bearings with specific grease that ensure maximum lifetime even at very high speeds.
③High Power
Compared to brush DC motors, brushless DC motors can carry a large current and thus show differences in rotational power.
If a high current is applied to a brush DC motor, the contact points between the commutator and the brushes may melt, resulting in failure. Therefore, it is difficult to achieve High Power.
Brushless DC motors do not have brushes, so there is no risk of contact melting. The advantage of brushless DC motors is that it is easy to achieve high power by applying a large current.
④Energy Saving Performance
Brushless DC motors offer better energy saving performance than brush DC motors. This is because brushless DC motors have a higher efficiency therefore and consume less power.
Also, as mentioned above, brushless DC motors do not require frequent maintenance and replacement because the commutator and brushes do not wear out. It is a product that considers the resource environment in terms of reducing resource consumption.
However, unlike most products, Mabuchi Motor's brush DC motors are compact, high-power, and have excellent energy conversion efficiency.
Types of Brushless DC Motors
Brushless DC motors are divided into two types according to rotor structure.
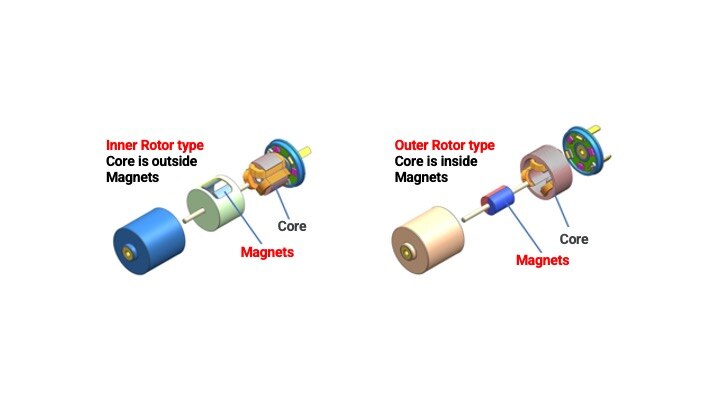
Surface Magnet Type (Outer Rotor Type)
A type of motor with permanent magnets attached to the outer circumference of the rotor is called a "surface magnet type" or SPM (Surface Permanent Magnet) motor.
The surface magnet type operates only by rotation (magnet torque) caused by the electromagnetic force between the rotor and the coil. Compared to the embedded magnet type, the surface magnet type has issues such as low rotational efficiency and magnet peeling due to centrifugal force, but it has the advantage of being easily miniaturized.
Embedded Magnet Type (Inner Rotor Type)
The type with permanent magnets embedded inside the rotor is the "embedded magnet type," also called an IPM (Interior Permanent Magnet) motor.
In addition to the magnet torque, the embedded magnet type brushless DC motor also utilizes the reluctance torque generated by the magnetic resistance.
Types of Sensors for Brushless DC Motors
There are three types of sensors that control the rotation of brushless DC motors: encoders, Hall sensors, and resolvers.
Encoders
Encoders are either magnetic or optical sensors built into the motor to accurately detect and measure the angular position of the rotor.
When used in conjunction with a Hallsensors, it can control motion with a high degree of accuracy. They are widely used in industrial robots such as factory assembly robots and unmanned transport machines.
Hall sensors
Hall sensors are smaller than resolvers.
Hall sensors, also called Hall elements, play a role in detecting the rotational position of rotor mainly to control the phase current switch.
The IS series is applicable to Mabuchi Motor's products. They can be used in a wide range of applications from consumer to industrial equipment.
Resolvers
Resolvers offer higher stopping accuracy and speed control with less rotation irregularity than Hall sensors. They are also more resistant to external factors such as heat, oil, dust, and vibration. They are superior to the Hall sensors in that they can be used in harsh environments.
The IR series is applicable to Mabuchi Motor's products. They are suitable for use in AGV and AMR used in warehouses and factories.
Mabuchi Motor also offers brushless DC motors that can be used in a wide range of applications. Please click here to see our product lineup.
Summary
This article has described the following information on brushless DC motors
- How Motors and DC Motors Work
- Overview of Brushless DC Motors
- Difference from Brush DC motors
- Types of Brushless DC Motors(Rotor structure / Sensor)
Brushless DC motors are a new type of motor that overcomes the problem of lifetime due to wear that has been a problem with conventional DC motors. They are expected to be used in a variety of fields and products because of their superior heat dissipation, high power, and energy savings as well as lifetime.
Mabuchi Motor is focusing on the development of brushless DC motors, and has a product lineup that incorporates "elements required for each application“, such as waterproofing, high-speed rotation, and quietness, while based on "compactness, light weight, and high efficiency”.
We also have a worldwide sales network and can deliver your desired product in a short period of time. We also provide consistent support from product selection to post-purchase, including requests for samples and confirmation of usage. Please feel free to contact us if you have any questions.