Understanding Motor Performance Terms: A Quick Guide
This guide explains common terms used in motor performance.
To choose the best motor for your product, it’s essential to understand these basic terms.
Let's review each term with an actual performance chart.
contents[非表示]
- 1.Basic Terms for Motor Performance
- 2.Explanation with Performance Specifications
- 3.FAQs
- 3.1.Is it safe to continue operating the motor beyond the rated voltage as long as it's within the operating voltage range?
- 3.2.When should instant maximum output and instant maximum torque be considered?
- 4.Conclusion
Basic Terms for Motor Performance
First, we'll look at three fundamental terms: torque, rotational speed, and output.
These terms are frequently used, so understanding them is key.
Torque [T] (Nm)
Torque, also known as twisting force, is the rotational power of the motor.
It means "The moment of force around a certain point when a force of 1N is applied perpendicular to that point, 1m away from the point. ".
It’s represented by the symbol T and measured in Newton meters (Nm).
Generally, increasing the current also increases the torque of the motor.
Rotational Speed [N] (r/min, rpm)
Rotational speed refers to how many times the motor's shaft rotates per minute.
It is represented by the symbol N and measured in revolutions per minute (r/min or rpm).
*Some motors may use revolutions per second (r/sec or rps).
Output [P] (W)
Output, also called mechanical power, refers to the amount of work done per second.
It’s represented by the symbol P and measured in watts (W).
The output is proportional to the product of torque and rotational speed and can be calculated with the following formula:
Output P (W) = 2π × Torque T (Nm) × Rotational Speed N (r/min) ÷ 60
≈ Torque T (Nm) × Rotational Speed N (r/min) ÷ 9.55
Efficiency [η] is the percentage of input electrical power converted to output mechanical power:
Efficiency η (%) = Output ÷ Input × 100
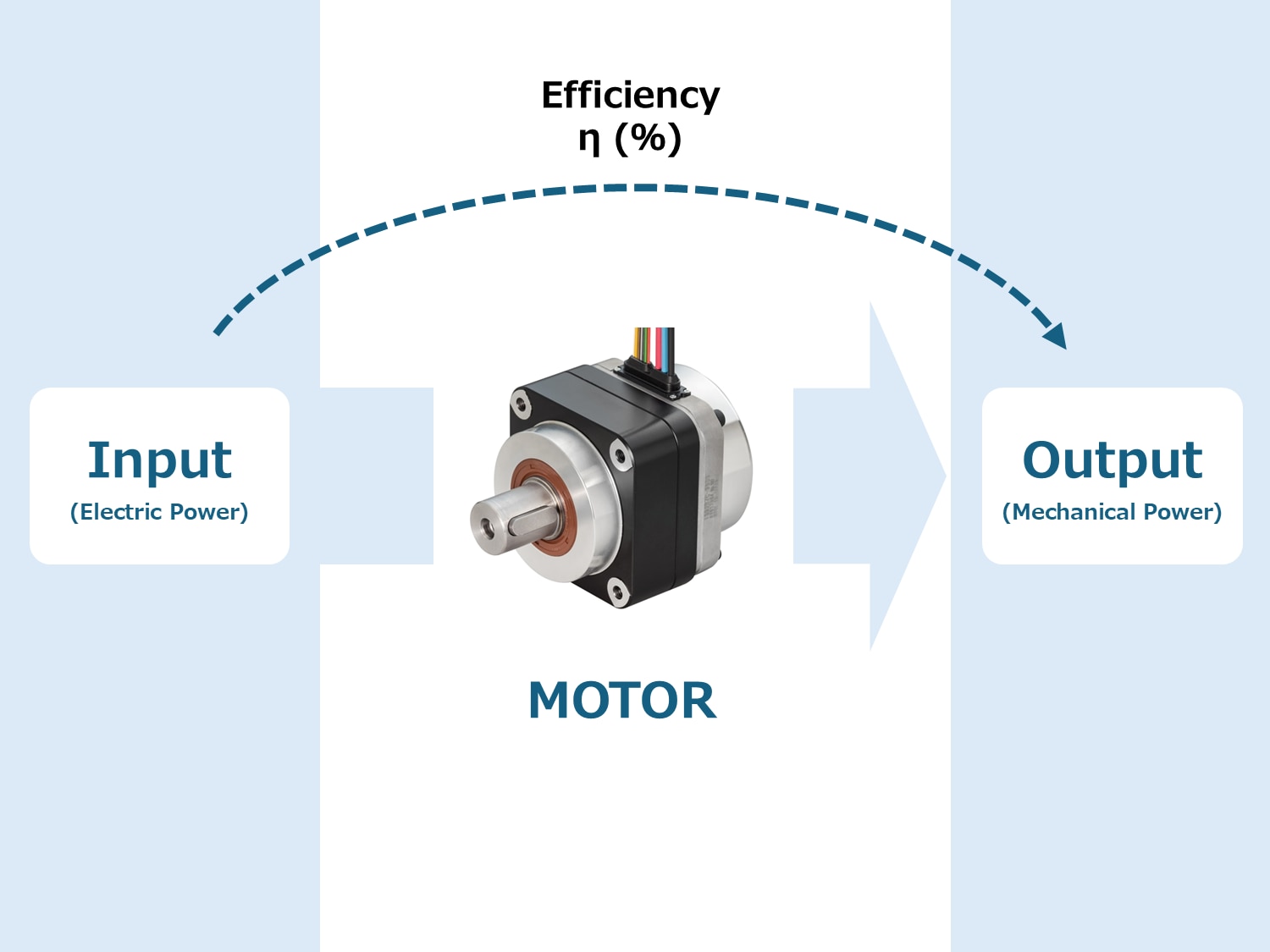
A flowchart illustrating motor efficiency, with electrical input (voltage x current) converting to mechanical output (torque x speed).
Explanation with Performance Specifications
Now, let's take a look at the performance chart of our brushless motor, the MS-94BZA, and go over each performance term.
Performance Spec | Terminology Guide | |
Instant Maximum Output | 342 W (10 sec max) | The maximum output that can be delivered momentarily. |
Instant Maximum Torque | 17.2 Nm (10 sec max) | The maximum torque that can be generated momentarily. |
Rated Voltage | 24 V | The recommended voltage for continuous and safe operation. |
Rated Power | 202 W | Mechanical output that can be delivered continuously and safely. |
Rated Torque | 8.6 Nm | Torque that can be generated continuously and safely. |
Rated Speed | 225 r/min | The speed at which the motor operates continuously and stably under the conditions of rated voltage and rated torque (load). |
Operating Voltage | 15-55V | The voltage applied to the motor during operation. The allowable voltage range is designed and predefined, and exceeding this range is not permitted. |
Size | 85.0 mm × 85.0 mm × Length : 84.5 mm | Motor Dimension |
Weight | 2.2 kg | Motor Weight |
Reduction Ratio | 10.33 : 1 | The gear (reducer) reduces the motor's output by decreasing rotational speed and increasing torque. This ratio is typically calculated as "input speed ÷ output speed" and is is generally greater than 1. |
Allowable Radial Load Bearing | 700 N | The maximum load that can be applied perpendicular (radial direction) to the motor shaft. |
Allowable Load Inertia | 0.6 kg / m2 max | The maximum load inertia that can be connected to the motor shaft while ensuring safe, stable operation, stopping, and control of the motor. |
Withstand Voltage | 500 V AC 1 minute | An indicator of the maximum voltage that the motor's components and materials can withstand. |
Insulation Resistance | 10 MΩ (min.) (500 V DC) | An indicator that represents the insulation performance of motor components and materials. |
Degree of Protection | IPx4 | The IP (Ingress Protection) rating indicates a motor's ability to resist water intrusion. An "IPX4" rating means the motor can withstand water splashes from any direction without compromising its normal operation. |
FAQs
In this section, we address common questions about motor performance terms.
Misunderstanding or misinterpreting these terms can lead to product failures or issues, so it’s important to be cautious.
Is it safe to continue operating the motor beyond the rated voltage as long as it's within the operating voltage range?
The motor can be used within the operating voltage range, but it is designed to operate at its rated voltage. For continuous and safe operation, we recommend using the motor at its rated voltage.
When should instant maximum output and instant maximum torque be considered?
These are important when lifting heavy loads, accelerating quickly, or when high torque is needed during startup. Insufficient torque at startup can cause delays in equipment activation, so be sure to check the instant maximum torque.
Conclusion
In this article, we provided a basic explanation of motor performance terms and further clarified each term by referring to the performance chart. Understanding these terms correctly is the first step in selecting the right motor for your application.
Mabuchi Motor offers a wide range of brushless motors to meet various needs. Please review the performance charts for each product and choose the motor that best suits your manufacturing requirements.
Explore our product lineup here.