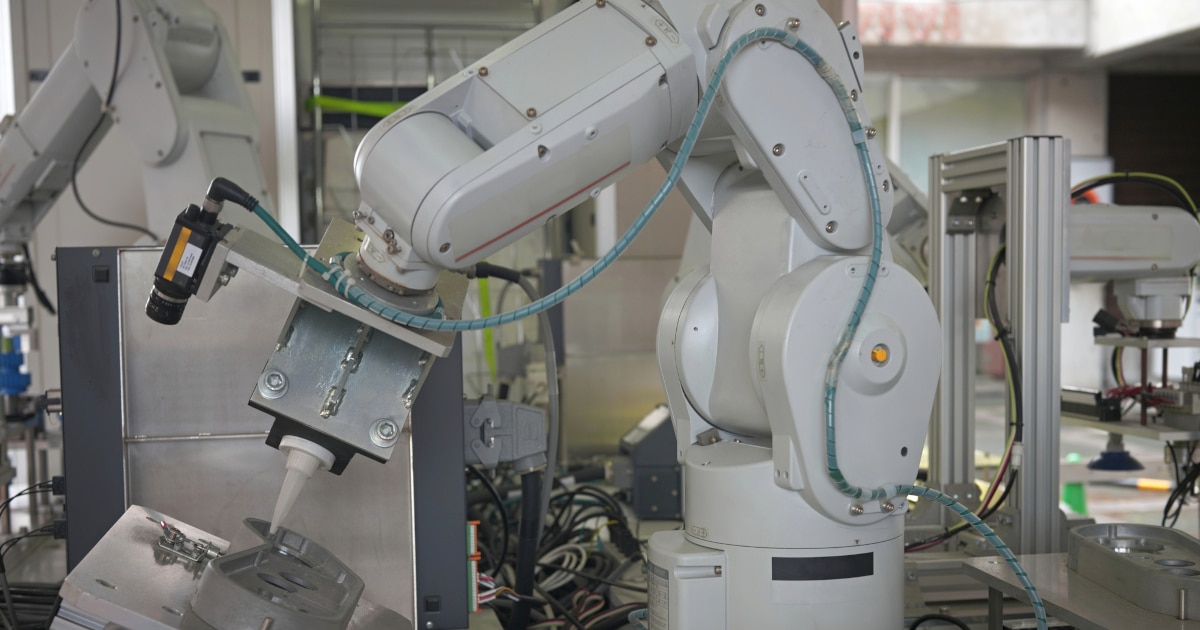
What is the Role of Collaborative Robots ? Explanation of the Differences from Conventional Industrial Robots
Recently, deregulation and technological advances have led to the introduction of collaborative robots at manufacturing sites for a wide variety of products, including food products and automobiles. But what exactly makes them different from conventional industrial robots?
This article explains the role of collaborative robots, how they differ from conventional industrial robots, and why they have attracted so much attention in recent years.
contents[非表示]
- 1. What is a Collaborative Robot?
- 2.Four Differences between Collaborative Robots and Conventional Industrial Robots
- 2.1.(1) Size and Weight of the Main Body of the Robots
- 2.2.(2) Tasks
- 2.3.(3) Installation Conditions
- 2.4.(4) Weight that can be Handled
- 3.Three Reasons Why Collaborative Robots Have Attracted Attention in Recent Years
- 3.1.(1) Deregulation of 80W Regulation in Japan
- 3.2.(2) Improvement of Safety Technology
- 3.3.(3) Ease of Introduction
- 4.Small Motors Suitable for Cooperative Robots
- 5.Summary
What is a Collaborative Robot?
Collaborative robots are highly safe robots that can work in the same area as humans. They can be operated in a flexible manner, for example, sharing the workload so that the collaborative robot can carry heavy parts and the human can assemble lighter parts.
Recently, they are being used not only in manufacturing, but also for serving food in the restaurant industry, and we are seeing more and more of them in our daily lives.
Note that although the term "collaborative robot" is sometimes seen, it is generally used in the same sense as "collaborative robot. In this article, we will use a unified notation for collaborative robot.
Four Differences between Collaborative Robots and Conventional Industrial Robots
Prior to the widespread use of collaborative robots, conventional industrial robots performed tasks in place of humans at manufacturing sites. Industrial robots were often used for simple tasks, mainly on large-scale, high-volume production lines, and people were not allowed to enter the areas where industrial robots worked, except for maintenance.
However, with the deregulation of robots in Japan in 2013 and advances in safety technology, collaborative robots that can be used for a wide variety of applications are now being introduced.
So what makes collaborative robots different from conventional industrial robots? Here are four specific items.
(1) Size and Weight of the Main Body of the Robots
Unlike conventional industrial robots, collaborative robots are characterized by their relatively small size and light weight. This reduces the risk of harm to people around them, even in the unlikely event of loss of control. It is this high level of safety that has made collaborative work with humans possible.
An equally small motor is essential for the smooth operation of small collaborative robots. Please see this article for more information on the features, types, and applications of small motors.
Introduction of Applications and Main Types of Small Motors
(2) Tasks
Most collaborative robots have about 5 to 6 axes of joints, enabling them to work at high speed and with high precision. As a result, they can handle tasks that require delicacy and can also support human operators.
Collaborative robots can also handle a wide variety of tasks. Collaborative robots are especially useful in the food manufacturing industry, where flexible response to variable production is required.
Conventional industrial robots excel at simple tasks and are often limited to the same type of product, while cooperative robots can handle a wide variety of tasks. Collaborative robots are especially useful in the food manufacturing industry, where flexible response to variable production is required.
(3) Installation Conditions
Installation conditions for collaborative robots and conventional industrial robots differ greatly depending on their size and whether they have safety fences.
The cooperating robots are compact and do not require safety fences to separate them from human workers, so they can be installed anywhere. They can be retrofitted to existing work lanes, which reduces costs and allows installation in small spaces.
On the other hand, industrial robots are large and require safety fences to separate dangerous areas. Therefore, it is necessary to secure a large space, such as a dedicated large lane, where only industrial robots can operate.
(4) Weight that can be Handled
Because of its light weight and small size, collaborative robost are not suitable for transporting or assembling heavy objects. As a guide, the line can handle up to 35 kg.
Conventional industrial robots are suitable for handling heavy products such as major automotive parts.
Three Reasons Why Collaborative Robots Have Attracted Attention in Recent Years
(1) Deregulation of 80W Regulation in Japan
One of the factors that has greatly promoted the spread of collaborative robots is the deregulation of industrial robots in Japan in 2013.
In the past, the use of industrial robots with an output of 80W or more was regulated, and the robots had to be fenced in and separated from the human workspace. However, this regulation was relaxed in 2013, and now robots with 80W or more output can work in the same space as humans as long as both the company and the user take measures in accordance with the standards set by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO).
This deregulation has expanded the range in which robots can be introduced, and has also accelerated the development of collaborative robots in Japan, leading to their further spread.
(2) Improvement of Safety Technology
Improved safety technology on the part of robot manufacturers is another reason why collaborative robots are beginning to attract attention.
Along with deregulation, risk assessment methods for working with robots have been developed, and manufacturers have improved their safety technologies in response.
As a result, safety is now ensured when robots work with humans, and the hurdles to introducing collaborative robots have been lowered, leading to their rapid spread.
(3) Ease of Introduction
The development of programs and applications to utilize collaborative robots is evolving and becoming easier to introduce, which is also encouraging the widespread use of collaborative robots.
The shorter preparation time and lower costs required to introduce robots have made it easier to introduce collaborative robots regardless of the size of the company.
In response to the increasing demand for such cooperative robots, Mabuchi Motor is promoting the supply of small motors for collaborative robots. Customers can choose either a hollow frameless type or a normal brushless type according to their requirements.
Small Motors Suitable for Cooperative Robots
There are several types of small motors. Which of these types is best suited for collaborative robots?
Here we will compare three typical types of small motors.
List of comparison results for ▼Small motors
(Date) Item |
Brushed DC Motor |
Stepper Motor |
Brushless DC Motor |
Life Span |
short |
long |
long (time) |
Power Efficiency |
midium |
low |
high |
Electromagnetic Noise |
high |
relatively low |
few |
Vibration |
relatively low |
high |
few |
Maximum Rotation Speed |
relatively low |
relatively high |
numerous |
The table shows that brushless DC motors are suitable for collaborative robots in many respects. Long life and high power efficiency are important for collaborative robots that perform continuous work for long periods of time. Low noise and vibration are also essential for collaborative robots that require precision in their work.
Mabuchi Motor's brushless DC motors are compact, lightweight, and highly efficient products. We offer a variety of products from our lineup to meet your collaborative robot applications.
For example, if you need high customizability for a wide range of applications, consider hollow frameless motor IA-IB series.
If stability at low speeds from a standstill is required, IR series, MR series, equipped with a resolver sensor that can detect the angle of rotation, is the best choice.
Summary
In this article, the following information on cooperative robots is described.
Applications of collaborative robots
How collaborative robots differ from conventional industrial robots
Reasons why collaborative robots are attracting attention
Small motors suitable for collaborative robots
Small and lightweight cooperative robots can safely support human work, thus contributing to cost reductions in manufacturing processes due to labor savings, as well as to the elimination of manpower shortages. High-performance small motors are necessary for the smooth operation of the collaborative robot.
Mabuchi Motor offers a wide variety of brushless DC motors, which are also available in our online store. If you are considering the type of motor, please feel free to contact us for the best proposal.