Electric motors are machines that convert electrical energy into mechanical energy. Definition implies that electric motors take electrical energy as input and provide mechanical energy as output.
Based on input electrical energy, motors are divided into two types: DC (direct current) motors and AC (alternating current) motors . These two types are further categorized into multiple types based on design and structure. They are utilized in various fields, including industries, automobiles, medical equipment, and robotics.
When purchasing a motor, some individuals may be uncertain about their selection. This article explains the features of DC and AC motors, highlighting the key differences between them. Furthermore, it will outline the appropriate applications for each type of motor, allowing you to choose your motor with confidence.
DC (Direct Current) Motors
DC Motors are motors that are powered by electricity flowing consistently in a single direction (direct current).
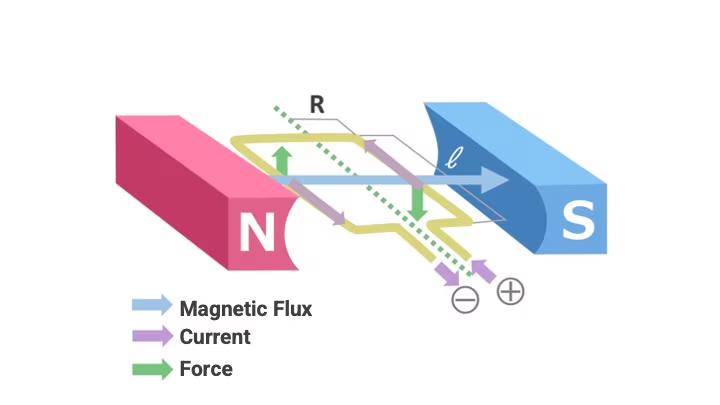
Figure1 : Principles of DC Motors
The electromagnetic force F and the torque
T of a DC motor can be expressed by the following formulas:
-
The electromagnetic force F is given by:
F = B・I・ℓ
where B is the magnetic flux (in Teslas), I is the current (in Amperes), and ℓ is the length of the conductor (in meters). -
The torque T is given by:
T = N・F・R
where N is the number of conductors, F is the electromagnetic force, and R is the distance from the center to the conductor (in meters).
Characteristics of DC Motors
The biggest feature of DC motors is that they can be powered by batteries . Since they can utilize portable batteries, they are suitable for applications such as automotive electrical devices, electric-assist bicycles, small household appliances, and power tools.
Types of DC Motors
DC motors can be classified into two types based on the presence or absence of brushes and commutators: brushed DC motors and brushless DC motors .
Brushed DC Motors
These motors generate rotation by switching the direction of current using brushes and a commutator. Their simple structure allows for low costs and ease of control. However, they also have downsides, including wear over time due to friction between the brushes and commutator, and noise generation.
Brushless DC Motors
By replacing the brushes and commutator with electronic circuits, brushless DC motors eliminate the disadvantages associated with brushed DC motors. Although they tend to be more expensive compared to brushed DC motors of the same power rating, their features include longer lifespan, higher efficiency, and quieter operation.
For more details on these motor types, view our comprehensive guide on brushed and brushless DC motors.
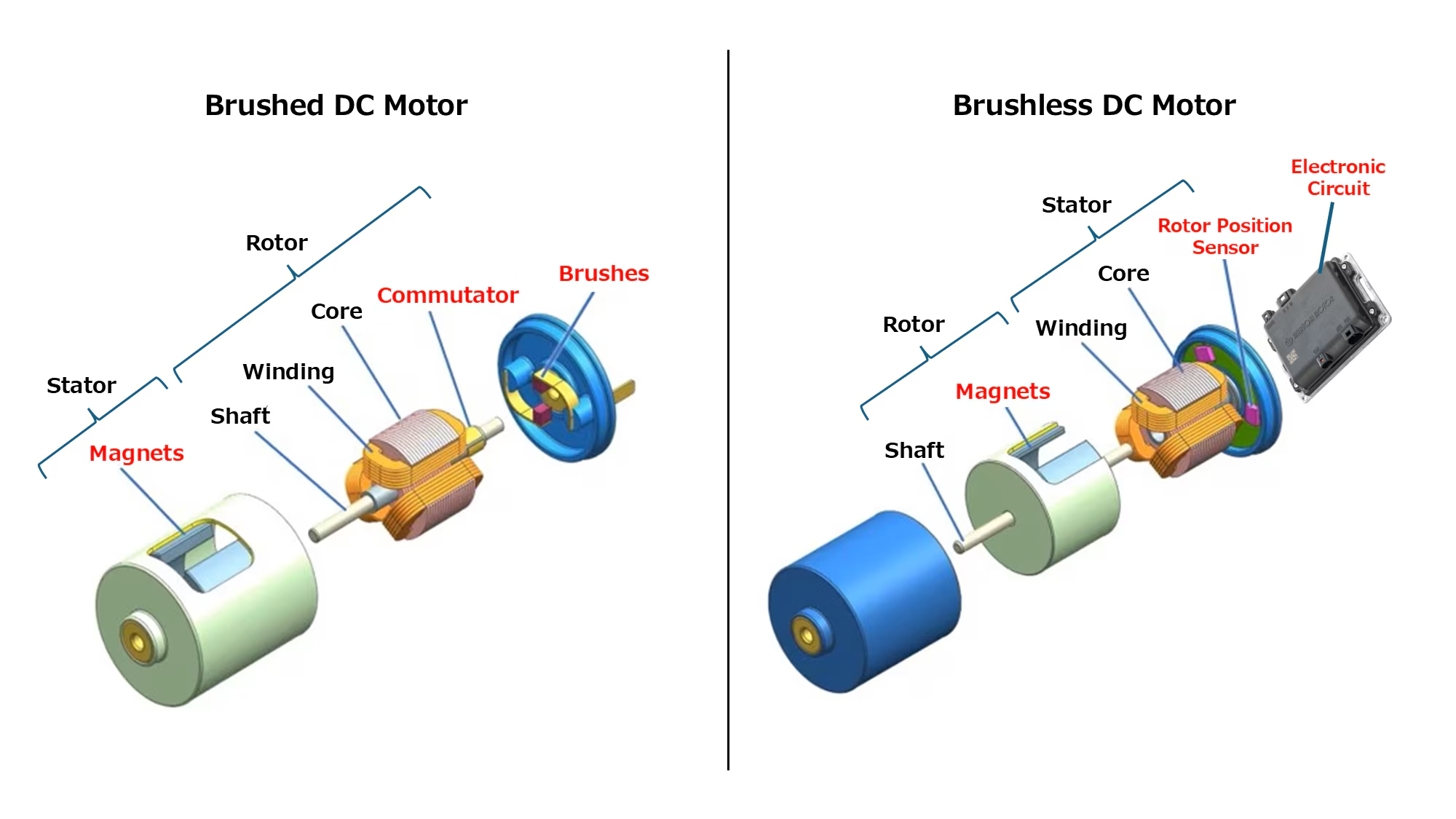
Figure 2 : Comparison of brushed and brushless DC motors.
(Left) A brushed DC motor uses brushes and a commutator. (Right) A brushless DC motor uses a sensor.
AC (Alternating Current) Motors
As the name suggests, AC motors are powered by AC current, which is periodic in nature and keeps switching direction.
Characteristics of AC Motors
The greatest feature of AC motors is that they can be directly connected to an alternating current (AC) power source for continuous operation.
In industrial and equipment applications, AC motors are often powered by three-phase AC power sources, providing large amounts of power to drive equipment such as elevators and large pumps.
In typical household applications, AC motors are frequently used in appliances that connect to single-phase AC power outlets.
Types of AC Motors
There are many types of AC motors, but they can primarily be categorized into two types used in industrial applications: synchronous motors and induction motors (also known as asynchronous motors) .
Additionally, there is a type known as single-phase AC motors, which are mainly used in household applications.
Synchronous Motors
Synchronous motors have coils in the stator and rotate at the same speed as the rotating magnetic field. The rotational speed is proportional to the frequency of the current, which is referred to as "synchronization."
Induction Motors
Induction motors, also called asynchronous motors, generate electromotive force in the coil through electromagnetic induction to produce rotation. While they also have coils in the stator, they differ in that the rotor consists of short-circuited coils. In the case of induction motors, the rotor rotates at a slightly lower speed than the rotating magnetic field produced by the stator.
Summary
It is important to carefully determine the necessary specifications based on the application, as DC motors and AC motors have different characteristics.
Mabuchi Motor develops and supplies brushed DC motors for automotive electrical equipment and home appliances, as well as "compact, lightweight, and high-efficiency" small brushless DC (BLDC) motors. Our BLDC product series offers optimal solutions for automation in industrial sectors and the development of high-performance medical devices.
If you are unsure about motor selection or would like assistance with selecting samples, please don't hesitate to contact us.